Trip Generation
IntroductionTrip Generation is the first step in the Sequential Demand Modelling arrangement which is also called as the Four Step Transportation Planning Process(FSTP) as mentioned earlier. In order to carry out modelling, the variable consists of total number of person-trips generated by a zone as a dependent variable and the independent variable consists of household and socio- economic factors which influence the trip making behaviour of the person. The data for the independent variable should be attained from an analyst. The output thus obtained consists of trip making or trip ends for each zone within a region.
In contemporary transportation planning language, A Trip is defined as a one way person movement by a mechanized mode of transport, having two trip ends. The start of the trip is called as origin and the end of trip is called as destination. Trip is classified as Production or Origin and Attraction or Destination. It should be note that the terminologies used are not identical. To understand with an example consider a single worker on a typical working day making a trip from his house which is in zone P to his office in Zone Q. Thus his trip origin will be zone P and trip destination will be zone Q. For the return trip from office to house his trip origin will be zone Q and trip Destination will be Zone P. Thus from the above Example it can be understood that the term Origin and Destination are defined in terms of direction of the trip while Production and Attraction in terms of land use associated with each trip end. Trip Production is the home end of home based trip and is the origin of trip of non home based trip. Trip Attraction is the non home end of home based trip and is the destination of a non home based trip.
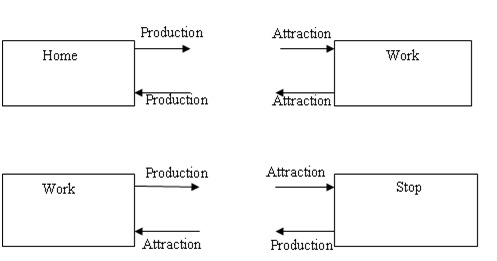
Classification of Trips
It has been found that better trip generation models can be obtained if the trips by different purpose are identified and modelled separately.The trips can be classified as given below:
1. Home Based Trip: One of the trip end is home.
Example: A trip from home to office.
Following are the list of home based trips that is trip purpose which are classified into five categories:
a. Work Trips
b. School Trips
c. Shopping Trips
d. Social- recreational Trips
e. Other Trips
The first two trips are mandatory trips while other trips are discretional trips. The other trip class encompasses all the trips made for less routine purpose such as health bureaucracy etc.
2. Non Home based trips: None of the trip end is home.
Example: A trip from office to Shopping Mall.
3. Time based trips
The proportion of journey is different by different purposes usually varies with time of the day. Thus the classification is often given as Peak and Off Peak Period Trip.
Example
| Time | Cars | Bus | Two Wheelers | Rickshaw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00 - 7:30 | 34 | 8 | 40 | 24 |
| 7:30 - 8:00 | 39 | 9 | 45 | 30 |
| 8:00 - 9:30 | 45 | 12 | 55 | 35 |
4. Person-type based trips
The travel behaviour of an individual is mainly dependent on its Socio-Economic attributes. Following are the categories which are usually employed.
a. Income Level- Poor, Middle Class, Rich
b. Car Ownership- 0,1,2,3
c. Household Size- 1,2,3,4... etc
Factors influencing Trip Productiona. No. of workers in a household.
b. No. of Students.
c. Household size and composition.
d. The household income.
e. Some proxy of income such as number of cars etc.
Factors influencing Trip Attractiona. Floor area and number of employment opportunities in retail trade, service, offices manufacturing and wholesale areas.
b. School and college enrolment
c. Other activity centres like transport terminals, sports stadium, major recreational/ cultural/religious places
Table below represents base year data of Trip Production for exact zone.
| Zone | Trips Produced | Home based trips(HBT) | Non Home based Trips(NHT) | Car Ownership(CO) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 50 | 35 | 12 |
| 2 | 150 | 45 | 36 | 35 |
| 3 | 127 | 36 | 23 | 34 |
| 4 | 150 | 57 | 36 | 58 |
| 5 | 170 | 48 | 55 | 35 |
Similarly Trip Attraction Table is obtained with respect to its influencing variables.
Trip generation study typically involves the application of residential trip production which contains variable that defines the demographic makeup of zonal population and trip attraction that captures the activity of non residential activities within the zone.
In the example given below the zones are connected by a two way link. Each zone will have its own demographic and non residential characteristics depending on which the Trip Generation table is represented below.
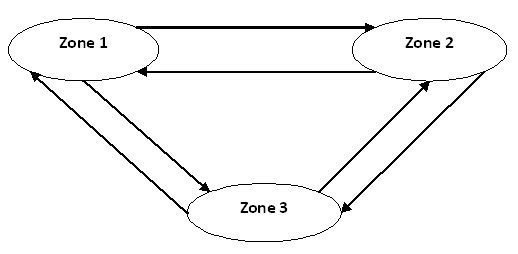
| Zone | Trips Production(P) | Trip Attraction(A) | |
| 1 | 2 | 20 | 34 |
| 2 | 2 | 25 | 25 |
| 2 | 1 | 35 | 55 |
| 2 | 3 | 67 | 70 |
| 3 | 2 | 55 | 75 |
The procedure to obtain the PA Table (shown above) from the base year condition of Trip Production and Attraction is explained in the next section call Modelling.
Modelling Trip Production
Modelling basically relates the dependent variable ie trips produced by a zone for aggregated model or household trip production rate for household based models to the corresponding Independent variables characterised by the whole zone or household characteristic respectively. Calibration is done based on the set of observations obtained corresponding to the zones for aggregate model and for disaggregate model employs a number of base year observations corresponding to an individual household in a sample of household drawn randomly from the region.
Thus we first need to identify what are the relevant variables:
a. Home end
b. Work End
c. Shop End
Analytical tools used for Trip Generation Modelling are given below:
1. Regression Model (Regression Analysis)
2. Cross Classification Model (Category Analysis)
The purpose of trip generation is to estimate the number of trip ends for each zones for the targeted year. The trip end is calculated for different travel purpose within the zone. These trips are represented as residential trip production obtained from household based cross classification tables or non residential trip attractions which is obtained by projection of land use. Trip generation Models that are often used are Multiple Linear Regression Model or Cross Classification Model or involves combination of both.
