| Civil Engineering Department |
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay |
 |
|||||
|
Research Areas Research Group Sponsored Research Research Facilities |
Owing to lower construction time and comparable costs, steel structures are used in the construction of industrial sheds, offshore structure, bridges and towers. In these type of structures, the beam and columns are often connected to each other using either bolted or welded joints. These joints, however, may degrade over time due to loosening of bolts,corrosion,weldcracks, etc. due to the types of loads that the structures are subjected to over that period of time. This structural degradation is often manifested through the change of material and/or geometric properties, which ultimately may define structural or functional damage. Therefore, a systematic study has been undertaken in order to develop a vibration based health monitoring technique for the estimation of damage at connections in steel structures.
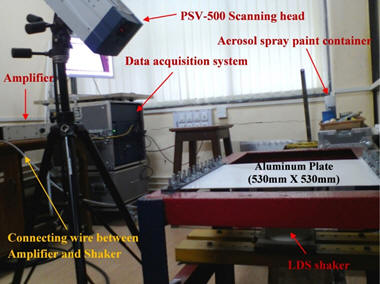
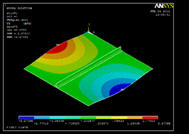
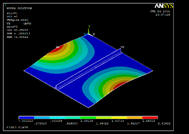
Reduction in strength due to debonding is a very common phenomenon in laminated composite plates or in between two metallic surfaces joined together by adhesives or weld. Therefore, development of efficient damage detection algorithms that would ensure early detection of damage, thereby, enforcing increased safety, durability and improved economic operation of the structures is a crucial task. Performance of some existing damage detection algorithms (e.g., Modal Curvature (MC), Gapped Smoothing Method (GSM), Generalized Fractal Dimension (GFD) and Wavelet Transform Coefficient (WTC)) have been studied in detecting debond in stiffened metallic plates. It has been observed that compare to other algorithms GFD is lesser noise sensitive, but, it produces false alarms. To alleviate this effect, some modifications has been proposed for GFD and it has been observed that new method performs outstandingly well in all circumstances. In this study, experimental investigation is performed using Laser Doplar Vibrometer (a non-contact sensing device) and LDS Permanent Magnetic Shaker (actuator). Extensive numerical simulations are further carried out using ANSYS 14.0 in order to examine the experimental findings. A study on damage severity has been performed, it is found that the proposed modifications of fractal dimension performs outstandingly well in all circumstances, and can be used as an excellent tool for debond localization and quantification.
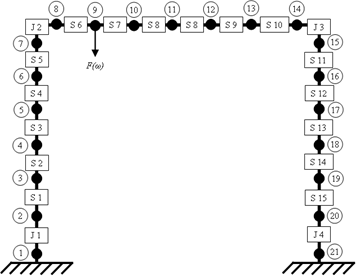
In the construction of civil engineering structures, two or more members are often rigidly connected to increase the structural integrity. These rigid joints are often designed with bolts, rivets and welding. The actions of in-service loading and environmental effects, or fabrication errors make these joints semi rigid, which ultimately reduces the structural reliability. Realistic dynamic analysis of these structures requires accurate modeling of rigidity of joints. Dynamic analysis of plane frames can be accomplished by combining spectrally formulated Rod and Euler-Bernoulli Beam element. A six parameter spectral plane frame joint element is formulated using linear and rotational springs to account for semi-rigidity of joints. Methodology and experimental set up for evaluation of dynamic characteristics of connections is formulated. The dynamic response of structure against impact and vibration is to be observed for semi rigid connections.
|
||||||

|
|||||||
|
Prof. Sauvik Banerjee, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076, Email- sauvik@civil.iitb.ac.in, Tel: +91-22-25767343. |
|||||||